Humans are complex creatures, with a wide range of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. They are capable of amazing things, such as creating art, inventing technology, and exploring the far reaches of space. At the same time, they can also be cruel, selfish, and destructive.
One of the defining characteristics of humans is their ability to communicate with one another. Through language, humans are able to share ideas, express emotions, and form social bonds. This ability has allowed humans to form complex societies and cultures, and to pass down knowledge from one generation to the next.
However, this ability to communicate also has its drawbacks. Misunderstandings, miscommunications, and even deliberate deception can all lead to conflict and mistrust. Humans are also prone to biases and prejudices, which can make it difficult for them to truly understand one another.
Despite these challenges, humans continue to strive for connection and understanding. They seek out relationships, both romantic and platonic, and work to bridge cultural and linguistic barriers. They create art that speaks to universal human experiences, and they use science and technology to solve problems that affect us all.
At the end of the day, humans are complex and imperfect beings, but they are also capable of great empathy and compassion. By recognizing our shared humanity and working to understand one another, we can create a better world for ourselves and future generations.
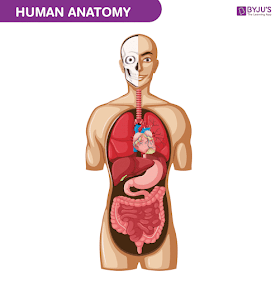
Anatomy of human body:
The human body is a complex and remarkable machine that is composed of numerous interconnected systems and organs. Understanding the anatomy of the human body is essential to maintaining good health and wellness.
At the most basic level, the human body is made up of cells, which are the building blocks of all living organisms. These cells work together to form tissues, which then combine to form organs. The organs are organized into systems, such as the respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems, which work together to keep the body functioning properly.
The skeletal system provides the framework for the body, with bones that protect vital organs and provide support for the muscles. The muscular system is responsible for movement and allows the body to perform physical tasks. The cardiovascular system, including the heart and blood vessels, circulates oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
The respiratory system, consisting of the lungs and airways, brings in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The digestive system breaks down food and extracts nutrients, while the urinary system removes waste products from the body. The nervous system controls and coordinates all of these functions, sending signals to and from the brain.
In addition to these systems, the human body also has specialized organs, such as the skin, which protects the body and regulates temperature, and the endocrine system, which produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Overall, the human body is a complex and interconnected system, with each part playing a vital role in maintaining health and wellness. Understanding the anatomy of the human body is key to maintaining good health, preventing illness and injury, and treating medical conditions when they arise.
The human body is a marvel of engineering and biology, with countless fascinating features and functions. Here are just a few highlights of the human body:
The brain: The human brain is the most complex organ in the body, with billions of neurons that allow us to think, reason, and experience emotions. It is responsible for controlling all bodily functions and coordinating the various systems of the body.
The heart: The heart is a powerful organ that pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the cells. It beats approximately 100,000 times per day and can continue to function even when other organs fail.
The lungs: The lungs are essential for breathing, taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the body. The lungs are also involved in regulating the body's pH balance and filtering out harmful substances.
The bones: The human body has over 200 bones that provide support, protect vital organs, and allow for movement. Bones are also involved in producing blood cells and storing minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
The muscles: The human body has over 600 muscles that work together to allow for movement and physical activity. Muscles are also involved in regulating body temperature and helping with digestion.
The immune system: The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from infections and diseases. It includes a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to identify and destroy harmful invaders.
The digestive system: The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and extracting nutrients that the body needs to function. It includes organs like the stomach, small intestine, and liver.
The skin: The skin is the body's largest organ, and it serves many functions, including protecting the body from the environment, regulating temperature, and producing vitamin D.
Overall, the human body is a complex and fascinating machine, with countless amazing features and functions that work together to keep us healthy and alive.
The human skeleton is a complex and intricate structure that provides support, protection, and mobility to the body. It is made up of 206 bones, each with a unique shape and function. Here are some key features of the human skeleton:
Axial skeleton: The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, spine, and ribcage. It provides support and protection to the body's vital organs, including the brain and spinal cord.
Appendicular skeleton: The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the arms, legs, pelvis, and shoulder girdle. It provides mobility and allows us to perform a wide range of physical activities.
Joints: Joints are the areas where bones come together and allow for movement. There are several types of joints in the human body, including hinge joints, ball-and-socket joints, and pivot joints.
Ligaments: Ligaments are strong, fibrous tissues that connect bones to other bones and provide stability to joints.
Cartilage: Cartilage is a flexible, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones and helps to cushion joints and reduce friction.
Bone marrow: Bone marrow is a spongy tissue found inside bones that produces red and white blood cells.
Cranial bones: The skull is made up of several cranial bones that protect the brain, including the frontal bone, parietal bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone.
Vertebrae: The spine is made up of 33 vertebrae that provide support and protection to the spinal cord. The vertebrae are divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal.
Overall, the human skeleton is a remarkable structure that provides the foundation for our bodies and allows us to perform a wide range of physical activities. By understanding the structure and function of the skeleton, we can better appreciate the incredible complexity and resilience of the human body.


No comments